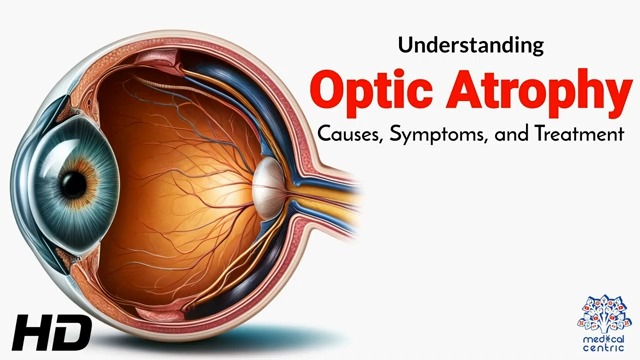
Optic atrophy is the degeneration or damage of the optic nerve, which can lead to vision loss. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Optic Atrophy

Optic atrophy can result from various factors that damage the optic nerve. Key causes include:
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure within the eye that damages the optic nerve.
- Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: Reduced blood flow to the optic nerve.
- Optic Neuritis: Inflammation of the optic nerve often associated with multiple sclerosis.
- Trauma: Injury to the optic nerve from accidents or surgery.
- Tumors: Pressure on the optic nerve from tumors in or around the eye.
- Hereditary Conditions: Genetic disorders like Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy.
Symptoms of Optic Atrophy
Symptoms vary depending on the extent of nerve damage. Common symptoms include:

- Vision Loss: Gradual or sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Reduced Visual Acuity: Blurred or dim vision.
- Color Vision Deficiency: Difficulty distinguishing colors, particularly reds and greens.
- Peripheral Vision Loss: Loss of side vision leading to tunnel vision.
- Optic Disc Pallor: Pale appearance of the optic disc observed during an eye examination.
8 Gym Machines That Could Be Harming Your Progress
Risks Associated with Optic Atrophy
Several factors increase the risk of developing optic atrophy, including:

- Age: Older adults are more susceptible to conditions that cause optic atrophy.
- Family History: Genetic predisposition to optic nerve diseases.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
- Neurological Disorders: Diseases affecting the central nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis.
- Eye Diseases: Conditions like glaucoma and severe infections.
Vision Aids
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluations and tests:

- Comprehensive Eye Exam: Assessing vision and examining the optic disc.
- Visual Field Test: Measuring peripheral vision.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Imaging to view the optic nerve and retina.
- MRI or CT Scan: Imaging to detect underlying causes like tumors or brain lesions.
- Blood Tests: Checking for underlying systemic conditions or infections.
Treatment Options
- Addressing Underlying Causes: Managing conditions like glaucoma, diabetes, or hypertension to prevent further damage. Treating infections or inflammation with appropriate medications.
- Vision Aids: Using glasses or contact lenses to improve remaining vision. Low vision aids like magnifiers and special lenses.
- Supportive Therapies: Visual rehabilitation training to adapt to vision loss. Occupational therapy techniques to maintain independence in daily activities.
- Medications: Corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory drugs for optic neuritis.
Prevention and Management

- Regular Eye Checkups: Early detection and management of eye conditions.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Keeping diseases like diabetes and hypertension under control.
- Protective Eyewear: Using safety glasses to prevent eye injuries.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.
Thank you for reading our article. Please do not forget to like and share this post.
For best traverling tips, Please visit